Intermittent fasting is a popular way to lose weight that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Think of it as giving your body some downtime between meals instead of snacking all day long. During the eating phase, you can enjoy your meals within a certain calorie limit, but when you’re fasting, you’ll restrict your intake and give your body a chance to tap into its energy reserves (a.k.a. stored fat).
While intermittent fasting is often seen as a go-to for shedding pounds, it’s also linked to other potential health perks, like better blood sugar control, reduced inflammation, and even improved brain function. But remember, everyone’s body reacts differently, so what works for one person might not work for another.
So, What Exactly Is Fasting?
In a nutshell, fasting means taking a break from food and drink that contain calories for a set amount of time. It’s not just about skipping meals—it’s about adjusting your eating pattern to allow your body to burn fat more efficiently. By limiting your eating window and extending your fasting period, your body shifts from relying on easy-to-access glucose (sugar) to burning stored fat for energy. Sounds cool, right? But hold on—it’s not a magic bullet, and it might not be for everyone. Age, sex, overall health, and lifestyle all play a role in how your body handles fasting, so it’s important to consider these factors before diving in.
Dr. Sara Gottfried, MD, emphasizes that intermittent fasting should be individualized. She explains that different bodies respond differently to fasting, especially when it comes to hormonal balance and metabolism. Adjusting fasting schedules based on personal needs and consulting with a healthcare provider can help make fasting more effective and sustainable.
Different Types of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is incredibly flexible, which is why it’s become so popular—there’s a method for almost everyone. If you’re considering giving it a try, it’s important to find a fasting style that fits your lifestyle and goals. Here’s a closer look at some of the most popular intermittent fasting methods:
16:8 Fasting
The 16:8 method is one of the most beginner-friendly and widely practiced forms of intermittent fasting. In this approach, you fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window each day. For many, this means skipping breakfast and having their first meal around noon, then finishing their last meal by 8 PM. The idea is to reduce the overall number of hours you spend eating, which can naturally lead to consuming fewer calories without the need for strict dieting. During the 16-hour fasting period, you can drink water, black coffee, and other non-caloric beverages to stay hydrated and curb hunger pangs.
Who It’s Good For: 16:8 fasting is great for people who are new to fasting and looking for an easier, more sustainable approach to cut back on calories. It’s also a good fit for those who like to eat larger meals but want to limit late-night snacking.
Challenges: While skipping breakfast might be convenient for some, others may find it hard to adjust, especially if they’re used to morning meals or have a physically demanding routine. It’s also easy to overeat during the eating window if not mindful of portion sizes.
5:2 Fasting
The 5:2 fasting method involves eating normally five days of the week and significantly restricting calories on the other two days. On fasting days, you usually limit yourself to about 500-600 calories. These fasting days aren’t consecutive—most people spread them out, like fasting on Monday and Thursday. During the fasting days, it’s not about completely avoiding food, but rather about mindful eating and choosing low-calorie, nutrient-dense options to get through the day.
Who It’s Good For: This method works well for people who don’t want to fast every day but are still looking to create a calorie deficit over the course of the week. It allows for more flexibility in daily eating habits while still offering the benefits of fasting.
Challenges: The 5:2 fasting method requires more planning, as you need to prepare for lower-calorie days. It can also be tough to stick to such low calories, and some people might struggle with energy levels on fasting days.
24-Hour Fasting (Eat-Stop-Eat)
The 24-hour fasting method, also known as Eat-Stop-Eat, involves fasting for a full 24 hours once or twice a week. For example, if you finish dinner at 7 PM, you wouldn’t eat again until 7 PM the next day. During this period, you’re allowed to drink water, tea, black coffee, and other calorie-free beverages to keep hydrated and help manage hunger. This method can be more intense because of the longer fasting period, but it’s also straightforward—you simply don’t eat for a whole day.
Who It’s Good For: This method is for those who are looking for a more significant calorie reduction but prefer not to fast every day. It’s also appealing to those who like the idea of a clear boundary—one day on, one day off.
Challenges: 24-hour fasting can be quite challenging, especially for beginners. Hunger and fatigue can be significant, and it might not be suitable for people with certain medical conditions or who have a high energy demand from work or exercise.
OMAD (One Meal a Day)
OMAD stands for “One Meal a Day,” which pretty much says it all. In this method, you’ll fast for 23 hours and eat all your daily calories in one single meal, typically within a one-hour window. Some people use this method to simplify their eating routine or because they prefer having one large, satisfying meal. OMAD is one of the more extreme forms of intermittent fasting, requiring strong willpower and the ability to maintain a balanced diet within one meal.
Who It’s Good For: OMAD might appeal to people who are busy and prefer not to think about eating multiple times a day. It can also work for those who enjoy large meals and find it easier to maintain a caloric deficit by eating just once.
Challenges: OMAD can be tough on the body and mind. It’s easy to feel overly hungry, and there’s a risk of overeating or making poor food choices due to intense hunger. It can also be difficult to get all the necessary nutrients in one meal, making it important to plan that single meal carefully.
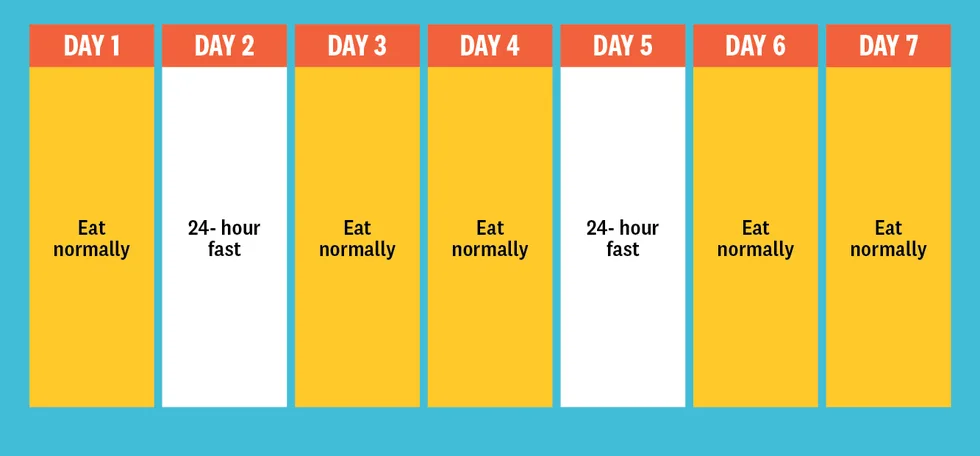
Alternate-Day Fasting
In alternate-day fasting, you alternate between a day of eating normally and a day of fasting. On fasting days, some versions allow for a very small amount of calories (around 500), while others recommend full fasting without any caloric intake. This method can be quite effective for weight loss and improving metabolic health due to the significant calorie reduction.
Who It’s Good For: Alternate-day fasting can be suitable for those who want a more aggressive approach to weight loss and don’t mind the intensity of fasting every other day. It’s also ideal for those who prefer a structured routine with clearly defined fasting days.
Challenges: This method can be difficult to maintain in the long term due to the frequency of fasting. It can lead to low energy levels, mood swings, and potential overeating on eating days if not managed properly.
Important Things to Keep in Mind
Before you jump on the fasting bandwagon, it’s a good idea to chat with a nutritionist or your doctor. Fasting might not be the best fit if you have certain medical conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or have a history of eating disorders. Plus, everyone’s body responds differently, so getting a professional opinion can help you tailor the approach to your needs.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Here’s the scoop on some of the potential benefits of intermittent fasting, but keep in mind that these can vary from person to person:
- Better Sleep: Believe it or not, fasting might help you sleep better. Aligning your eating schedule with your body’s natural rhythms can help regulate your sleep-wake cycle. Just be mindful of meal timing—eating too close to bedtime can sometimes mess with your sleep.
- Weight Loss: One of the main reasons people try fasting is to lose weight. By shortening your eating window, you’re likely to eat fewer calories overall, which can help with weight management. Plus, fasting can encourage your body to burn fat for energy instead of just using up what you ate recently.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Fasting might help your body become more sensitive to insulin, which is super important for keeping your blood sugar levels stable. This can lower your risk of type 2 diabetes over time, which is a big win!
- Better Heart Health: Some research suggests that intermittent fasting can have a positive impact on heart health by helping lower blood pressure, reduce bad cholesterol (LDL), and decrease inflammation. Of course, this depends a lot on what you’re eating during your non-fasting periods, so balance is key.
- Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is linked to a bunch of health problems, including heart disease and cancer. Some studies show that fasting can help reduce inflammation, which might help lower your risk of these conditions.
- Boosts Brain Function: There’s some early research suggesting that intermittent fasting might be good for your brain, too. It could help improve memory and even support the growth of new nerve cells, which is pretty amazing.

How to Get Started with Intermittent Fasting?
Thinking of giving fasting a try? Here’s a quick guide to help you ease into it:
Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to how your body feels during fasting. If you’re constantly tired, dizzy, or just not feeling great, it might be a sign to tweak your approach or take a break from fasting altogether.
Consult a Pro
It’s always smart to get some expert advice before starting a new diet. A nutritionist or doctor can help you figure out which fasting style might work best for you and make sure it’s safe based on your health background.
Pick a Method That Fits Your Lifestyle
Not everyone is cut out for 24-hour fasts or eating one meal a day. Start with a gentler approach, like the 16:8 method, and see how your body handles it.
Ease In Slowly
If you’re used to eating throughout the day, don’t jump into an extreme fasting schedule overnight. Gradually extend your fasting window and see how you feel.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking water is a must, especially during fasting periods. You can also sip on calorie-free beverages like herbal teas or black coffee to help keep hunger at bay.
Eat Well When You’re Not Fasting
Fasting isn’t an excuse to eat junk food during your eating window. Focus on nutrient-dense foods—think lean proteins, veggies, whole grains, and healthy fats—to keep your energy up and nourish your body.

Foods That Work Well with Fasting
What you eat during your eating window matters—a lot. Here are some foods that can help you make the most of your fasting routine:
- Fruits and Veggies: These are your go-to for fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Fresh options like berries, apples, leafy greens, and bell peppers are all great choices.
- Protein Sources: Don’t skimp on the protein—lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins like beans and lentils can help keep you full and satisfied.
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil are awesome sources of healthy fats that can keep you feeling full longer.
- Whole Grains: Incorporate whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread to keep your energy up and provide lasting fullness.
- Hydration Heroes: Water, herbal teas, and calorie-free drinks should be your best friends. Staying hydrated is key, especially when you’re fasting.
cocnclusion
Intermittent fasting can be a helpful tool for weight loss and improving some health markers, but it’s not the magic answer for everyone. Success with fasting hinges on balance—eating nutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and paying attention to your body’s needs. And remember, it’s always best to get the green light from a healthcare provider before making major changes to your eating habits. Whether you’re just curious or ready to dive in, intermittent fasting is all about finding what works for you and making it part of a healthy lifestyle.
Related posts: